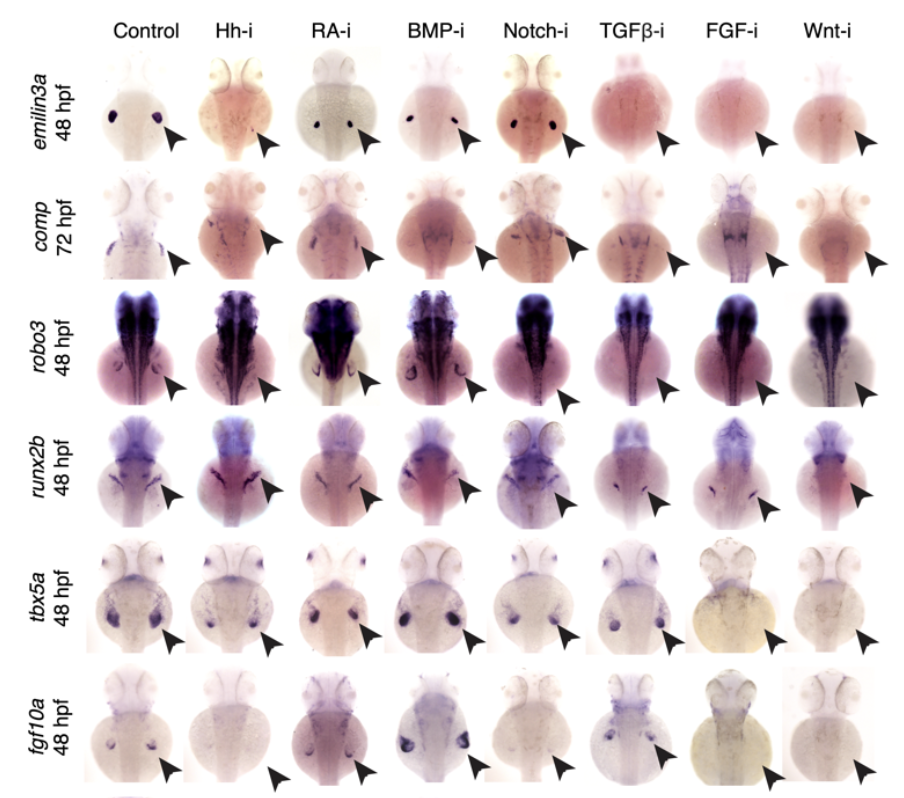
Abstract
Organogenesis is a highly organized process that is conserved across vertebrates and is heavily dependent on intercellular signaling to achieve cell type identity. We lack a comprehensive understanding of how developing cell types in each organ and tissue depend on developmental signaling pathways. To address this gap in knowledge, we captured the molecular consequences of inhibiting each of the seven major developmental signaling pathways in zebrafish, using large-scale whole embryo single cell RNA-seq from over two million cells. This approach allowed us to detect signaling pathway regulation even in very rare cell types. By focusing on the development of the pectoral fin, we uncovered two new cell types (distal mesenchyme and tenocytes) and multiple novel signaling dependencies during pectoral fin development. This resource serves as a valuable tool for investigators seeking to rapidly assess the role of the major signaling pathways during the formation of their tissue of interest.
One Sentence Summary:
Using large-scale single-cell RNA-seq in zebrafish embryos, researchers mapped the effects of inhibiting seven major developmental signaling pathways, uncovering new cell types and signaling dependencies—especially in pectoral fin development—offering a valuable resource for studying organogenesis.
** corresponding authors